The US military is no stranger to 3D printing, having supported and developed a plethora of AM breakthroughs. Though they certainly work with metal 3D printing, officers like the accessibility and readiness of traditional filament deposition 3D printers that can be easily moved around in the field. FDM printers aren’t known for making the strongest of parts, though, and if anyone needs strong parts it’s the military. Fortunately, they’re an ingenious bunch.
Dr. Eric D. Wetzel of the Army’s Emerging Composites team led the project to create a stronger filament. The team fabricate a billet of material comprising ABS, with a star‐shaped PC (polycarbonate) core. That column is then put into a machine called a thermal draw tower that heats one end and draws it out into a thin filament that’s cooled and spooled for later use on any FDM 3D printer. The new filament consists of ABS and PC so the DM (dual-material) parts are annealed after printing to completely fuse the two materials, maximizing the strength and heat deflection temperature.
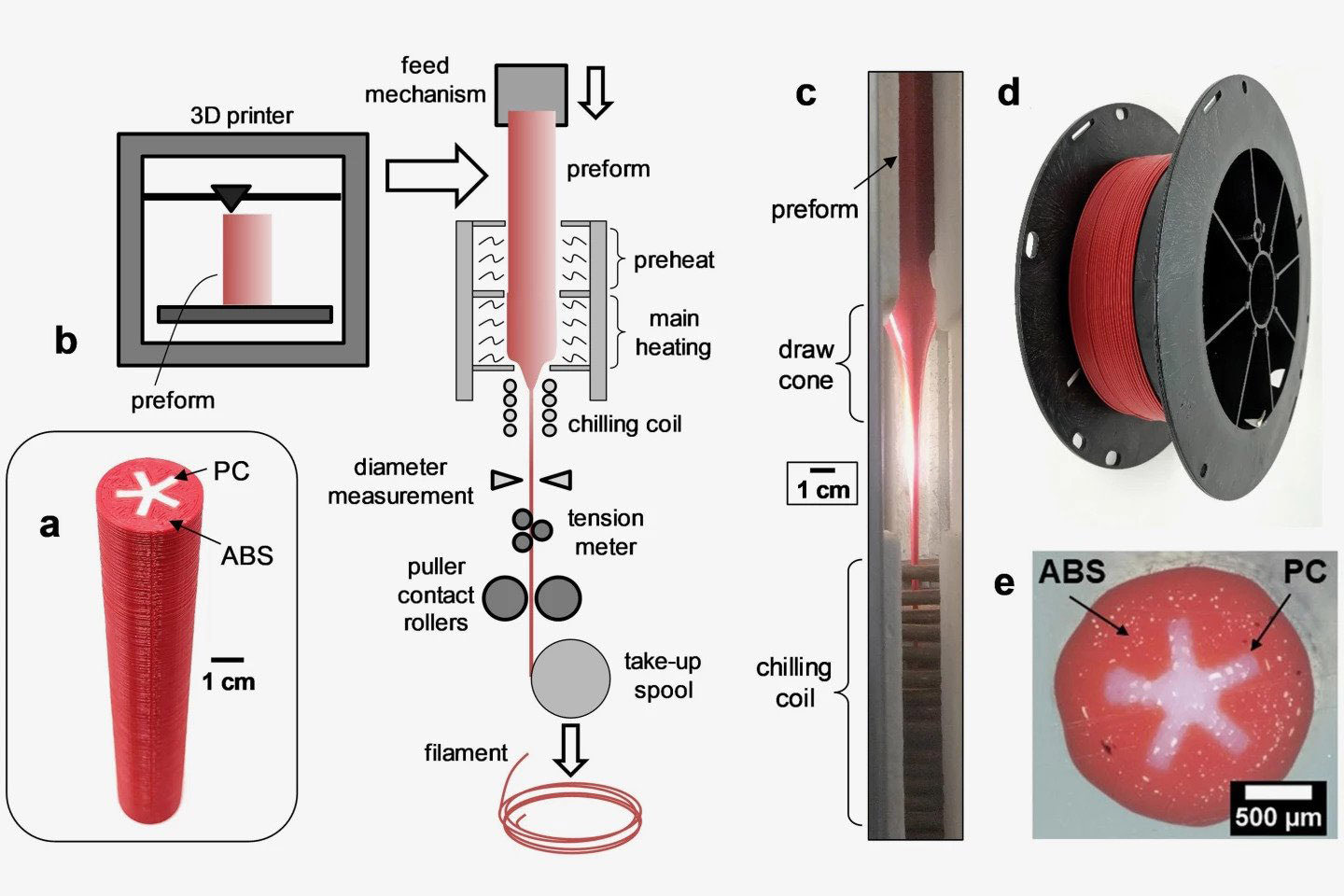
Tests revealed that the DM parts have ductility that’s similar to injection molded ABS parts and have fracture toughness values 15 times higher than comparable printed ABS parts. And there’s little shrinkage or warping that occurs during the annealing process because the “PC skeleton of specimens fabricated using the DM filament resists creep and polymer relaxation to maintain accurate part geometry during annealing.”
The engineers tried eight different shapes for the PC core, including a circle and different numbers of spokes but the asterisk shape exhibited the best mechanical properties. With more research from 3D printing and materials companies that the Army is requesting, this could lead to significantly stronger parts for everyone with an FDM printer. In the paper published in the journal Advanced Engineering Materials, the authors use no uncertain terms, “This novel DM filament can revolutionize additive manufacturing allowing low‐cost printers to produce parts with mechanical properties competitive with injection‐molded plastics.”
Source: US Army Research Laboratory