Researchers at Virginia Tech have just achieved a groundbreaking new 3D printing method. Using mask-projection micro-stereolithography, they have printed the highest temperature polymer to date. The material, Kapton, is an aromatic polyamide that has multiple applications which require high-durability. One of its uses is as spacecraft insulation.
The researchers insist that 3D printed Kapton has a strength comparable to those made by traditional methods. Katpon begins to lose its mechanical properties at 1,020 °F (548.8 °C). As a result, the new printing method achieves temperatures 285 °F higher than any other polymer would need.
Mask-Projection Micro-Stereolithography
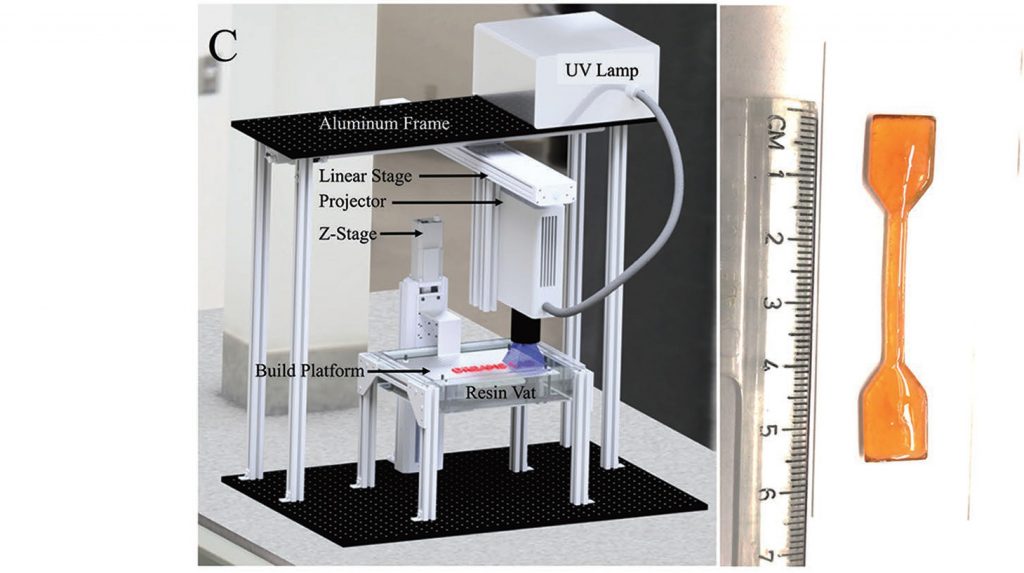
Mask-projection micro-stereolithography is an SLA method. Typically the method uses a broad spectrum light source to cure photopolymers by projecting 2D images using a Digital Micromirror Device. The hardware and operating software are very malleable and thus researchers can apply it to various applications and materials.
While we do not know what printer they used, the researchers at Virginia tech have Mask-projection micro-stereolithography machines like the Autodesk Ember in their lab. Mask-projection micro-stereolithography generally use UV, like most SLA devices. Additionally, like other forms of SLA (aside from constrained surface stereolithography), it places the UV projector above a descending platform, that unveils the print vertically.
Applications
Applications of the material include space insulation and spacecraft parts. NASA and other space travel enterprises are very prominent users of 3D printing technologies. This is a natural step forward for their operations and will come into use use all the safety tests have been cleared.
Another possible use is is in bulletproof vests. Polyamides are the same class of material as kevlar. This can be a boon to law enforcement or arms manufacture industries. This is predicated on just how much more efficient this particular method and strain of material can be to those industries.
The method itself allows for a fast and efficient way to produce very powerful materials. Aside from Katpon, this method opens up new range of high-temperature resins. Considering the material strengths that it can achieve, with further research they could put it to use in all sorts of industrial applications.












